http://robertdunaway.github.io
Gulp code kata list
All code katas lists

024 Gulp - replace & passing params
Duration
15 minutes
Brief
In this kata we will rename constant values based on configuration files and parameters passed in.
For more information
BING/GOOGLE: “Gulp ”
Book:
Gulp - Quick guide to getting up and running today
Instructions
Get tutorial folder or the entire katas-Gulp repo.
Open the [before/*.sln] file and execute the kata.
Feel free to execute this kata multiple times because repetition creates motor memory.
Github
- Before (start kata with this)
- After
Kata
Most applications are expected to function in multiple environments. When coding you expect the application to function in the local environment. When you deploy to the test environment you expect it to function there and the same for production.
In this kata we will rename constant values based on configuration files and parameters passed in.
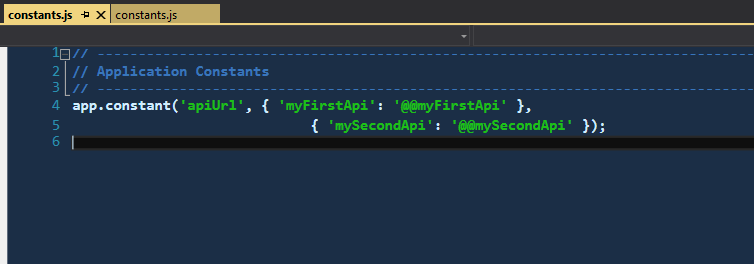
You have constant values in src/js/comstants.js. Change the values for @@myFirstApi and @@mySecondApi. Create three sets of config files. One for dev, stage and prod. You’re going to use the parameter --env and follow that with the environment you intend your build to be fore.
Example you will be able to use these gulp commands.
gulp --env-dev
or
gulp --env-prod
Review
Install the needed NPM packages.
npm install gulp-replace-task --save-dev
npm install yargs --save-dev
gulp-replace-task: Enables us to find and replace variables identified with “@@”.
yargs: Enables the use of command line parameters.
fs: Enables the ability to load local files.
Add references to the new modules to the gulpfile.
, replace = require('gulp-replace-task')
, args = require('yargs').argv
, fs = require('fs')
Create three config files in the src/config folder, for each environment.
env.config.dev.json
Create this file with the following content.
{
"myFirstApi": "http://devFirstApi",
"mySecondApi": "http://devSecondApi"
}
env.config.stage.json
Create this file with the following content.
{
"myFirstApi": "http://stageFirstApi",
"mySecondApi": "http://stageSecondApi"
}
env.config.prod.json
Create this file with the following content.
{
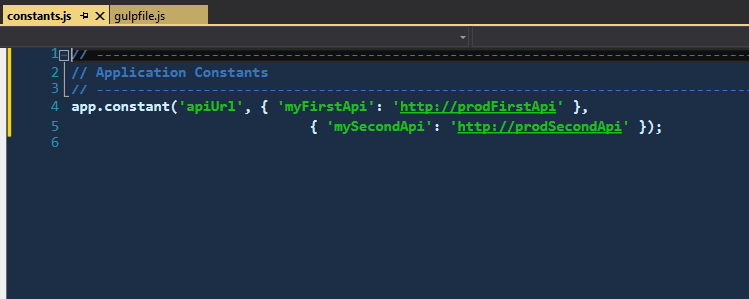
"myFirstApi": "http://prodFirstApi",
"mySecondApi": "http://prodSecondApi"
}
Create the setEnv task and update the default task to run it after src is copied.
gulp.task('setEnv', function () {
// Get the environment from the command line
var env = args.env || 'dev';
// Read the settings from the right file
var filename = 'env.config.' + env + '.json';
var settings = JSON.parse(fs.readFileSync('src/config/' + filename, 'utf8'));
// Replace each placeholder with the correct value for the variable.
gulp.src('src/js/constants.js')
.pipe(replace({
patterns: [
{
match: 'myFirstApi',
replacement: settings.myFirstApi
},
{
match: 'mySecondApi',
replacement: settings.mySecondApi
},
]
}))
.pipe(gulp.dest('wwwroot/js/'));
});
gulp.task('default', function () {
runSequence('copy-to-wwwroot', 'setEnv');
});
Executing the new task
The default parameter is dev so if you pass no parameters then the env.config.dev.json file is used.
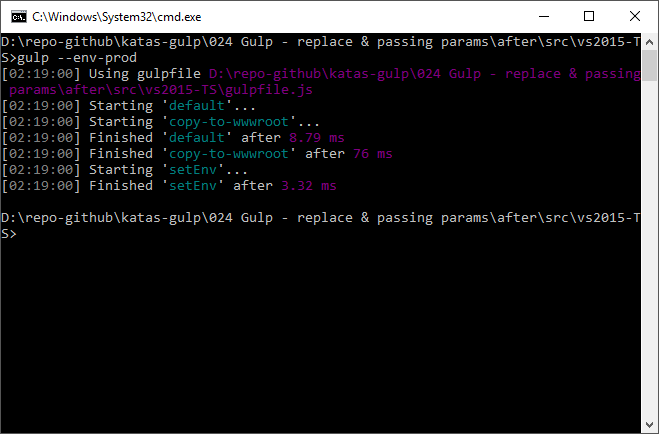
Here is the command-line syntax for updating the files with production values.
gulp --env prod
I’m not sure how to execute this in Visual Studio so for now you need to do this from the command line in the root folder of the solution. Visual Studio will likely develop the ability to pass parameters.
Before
After
Next
Take a few minutes and imagine more examples.







0 comments:
Post a Comment