http://robertdunaway.github.io
http://mashupjs.github.io
The Mashup is a learning tool that serves as a seed project for line-of-business applications. It’s goal is a shortened learning curve for building modern business applications and the reduction of technical debt.
This tutorial and more can be found in
Gulp - Quick guide to getting up and running today
Gulp Tutorial - Part 18
Useful NPM Tips
COMMANDS CHEAT SHEET
Find outdated modules
npm outdated -–depth=0
npm outdated –-json -–depth=0
Installing a package
npm install grunt-contrib-uglify@* --save-dev
Updating local packages
When someone has added modules since your last check-in just run.
npm update
POWERSHELL (PRIMER)
Windows users can use either the Command Prompt or PowerShell.
PowerShell is pre-installed on Windows 8 or newer installations.
From Start: Search programs and files type “powershell”. Select “powershell.exe”.
SYNTAX
Powershell Command Syntax:
application action –flags arguments
For help with any application add the –h or –help flags for additional instructions.
The tab key autocompletes your statement.
ADDING AND REMOVING FILES
To create a new item use the ni command. This might not seem useful with Visual Studio 2013 because any file added must also be added to your project file. Visual Studio 2015 does not have a project file needing updates. Instead a Glob pattern is used to determine what files should and should not be included in the project. That being the case, suddenly, ni makes more sense.
Adding files
ni newjsfile.js -type file
new-item newjsfile.js –type file
Removing files
ri newjsfile.js or remove-item newjsfile.js
INSTALLING NODEJS AND NPM PACKAGES
Install NodeJS from:
https://nodejs.org/
Install NPM packages with the following syntax
npm install [global option –g] [package-name] [options]
Example: (You need to install Gulp both locally and globally)
npm install gulp --save-dev
npm install gulp –g
https://docs.npmjs.com/getting-started/installing-npm-packages-locally
NPM VERSION UPDATES
There are multiple options for keeping NPM packages up to date. The approach you choose might depend on your development workflow and automated testing solution, i.e., if you have good automated testing, it might be safe to allow the latest versions. If not, you might want to choose a more deliberate approach to NPM versioning.
VERSION UPDATES: OPTION 1 – USING NODE TOOLS
Check to see which NPM packages are out of date
Display colored rows
npm outdated -–depth=0
Display in json which includes current, wanted, latest version numbers
npm outdated –-json -–depth=0
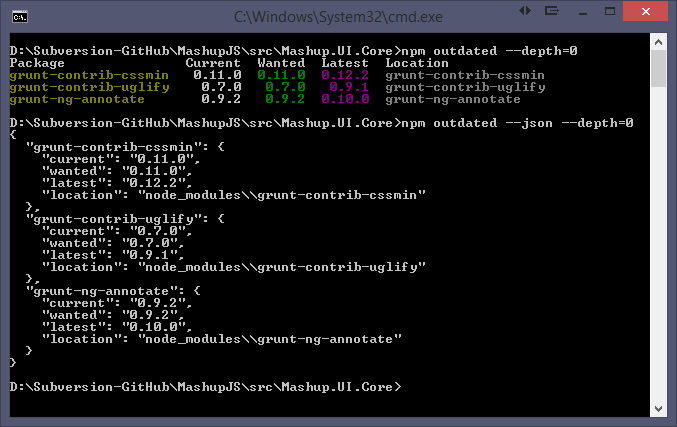
Note: Not all your packages will be displayed. Only the outdated packages will be displayed.
Note: If you modify the command to include “-g” then you’ll get a list of your outdated global packages.
To update packages one at a time
npm install [package-name]@* [save?]
npm install grunt-contrib-uglify@* --save-dev
VERSION UPDATES: OPTION 2 – USING NPM-CHECK-UPDATES
Using the npm-check-updates package, you can keep all your packages updated.
https://www.npmjs.com/package/npm-check-updates
npm install -g npm-check-updates
Then execute the following command to see what packages can be updated.
npm-check-updates
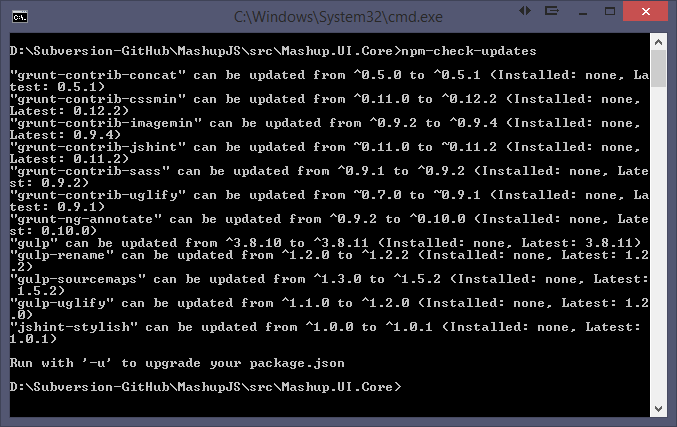
To upgrade all your packages
npm-check-updates –u [-g option for global packages]
Now your package.json is updated.
Then execute an NPM install to update the package installations.
npm install [-g option for global packages]
NPM VERSIONING SEMANTICS
https://docs.npmjs.com/misc/semver
http://semver.org/
Source code for this tutorial
Start the tutorial using this code base:
https://github.com/MashupJS/gulp-tutorial
A completed tutorial can be found here:
https://github.com/MashupJS/gulp-tutorial-end-result
This tutorial and more can be found in






0 comments:
Post a Comment